If you found yourself here looking up "ester ana onlyfans," you might be in for a little surprise, you know? This space is going to talk about something quite different, but just as interesting, in its own way. We're going to explore what an "ester" truly means, not in the way you might expect from a certain kind of search, but from a scientific point of view. It's a journey into the tiny parts that make up our world, and how they fit together.
It's rather fascinating how a simple search term can sometimes lead you down a completely different path, isn't that so? What we're about to talk about concerns a type of chemical compound that plays a big part in many things around us, often without us even realizing it. So, if you're curious about the building blocks of matter, or just stumbled here by chance, stick around.
We will be uncovering some basic facts about these compounds, what they are made of, and where you might come across them in your daily life. It’s a chance to learn something new, perhaps something you never thought about before, and maybe even connect it to those familiar smells and tastes that make up our everyday experiences.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Is a Chemical Ester, Anyway?
- How Are Esters Formed? Unpacking the Chemistry
- Where Do We Find Esters in Everyday Life?
- The Scent and Flavor of Esters – What About "OnlyFans"?
- Breaking Down Esters - Is "Ester Ana" a Compound?
- Understanding Ester Hydrolysis and Its Uses
- Why Are Esters Important?
- Naming Esters and What That Means for You
What Exactly Is a Chemical Ester, Anyway?
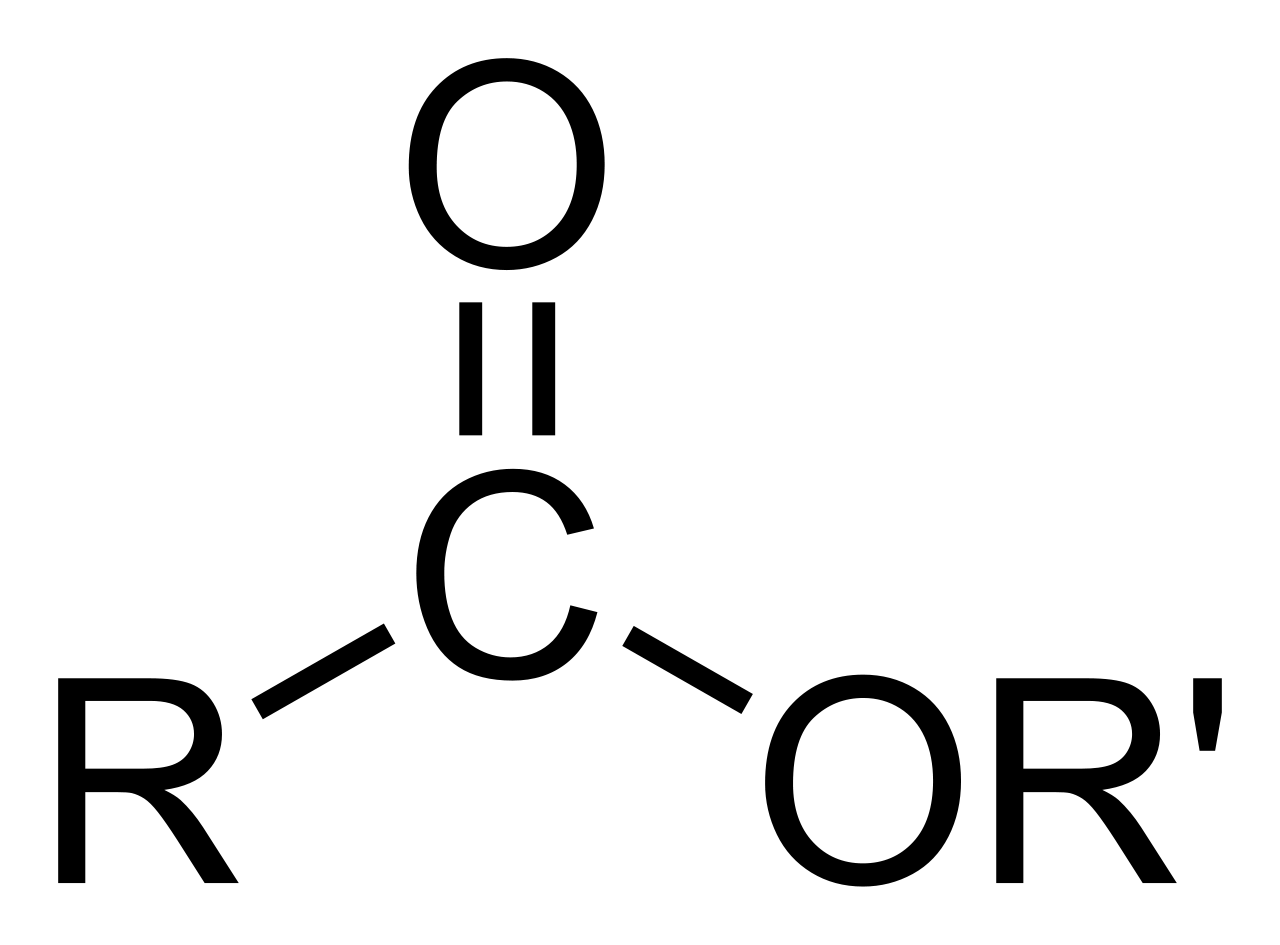
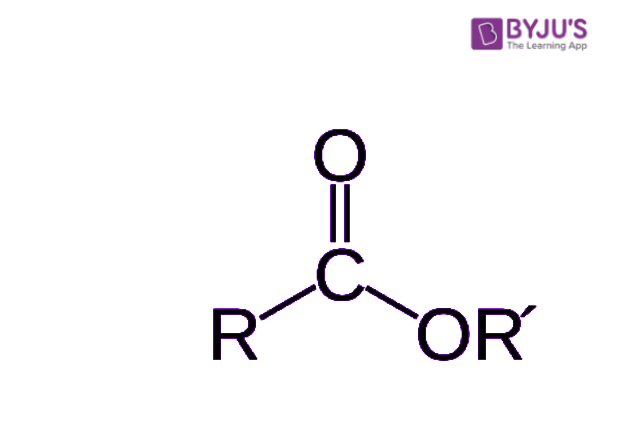
So, what exactly is an ester when we talk about chemistry, you might ask? Well, it’s a kind of chemical substance that comes from an acid. Think of it like this: acids, whether they come from living things or not, have a little piece that includes a hydrogen atom and an oxygen atom joined together. In an ester, this hydrogen atom gets swapped out for something else. It's almost like a tiny chemical swap meet, where one piece leaves and another takes its place.
These compounds are a particular group of organic substances. They have a special way of reacting with water. When they meet water, they break apart, creating two new things: an alcohol and either an organic acid or an inorganic acid. This process is actually pretty common in the chemical world, and it’s how we can sometimes get back to the original ingredients that made the ester. It's a bit like taking apart a toy to see its separate pieces, so to speak.
The most frequently seen esters are those that come from what we call carboxylic acids. These are a very usual kind of acid in organic chemistry. Knowing this general arrangement for an ester is a helpful first step, as a matter of fact. It helps you figure out what you are looking at when you see a chemical formula. There's a basic shape that most esters follow, and once you get that, a lot of other things start to make sense.
When we talk about an ester, we are really talking about an organic compound where a hydrogen piece in a specific part of the compound, called the carboxyl group, gets replaced. Instead of hydrogen, a hydrocarbon group moves in. This hydrocarbon part is basically a chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms. So, it's a specific kind of change that happens to an acid, giving us a new compound with some rather unique properties.
How Are Esters Formed? Unpacking the Chemistry
Esters are usually created from carboxylic acids, as we mentioned. The way they come into being is through a process that involves another type of compound called an alcohol. It's a bit like a chemical dance where an alcohol and an acid get together. During this coming together, a molecule of water is typically lost. This loss of water is a key part of the reaction that makes an ester. It’s a pretty neat trick that chemistry pulls off, creating something new by taking away a small piece, you know?
This kind of compound, a carboxylic ester, is also sometimes called a carboxylate ester. It’s just another name for the same thing, helping us describe this particular arrangement of atoms. The creation of these substances is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry. It shows how different groups of atoms can combine to make something entirely different, with its own set of characteristics. This process is, in some respects, a basic building block for making many other complex chemicals.
To give you a clearer picture, imagine an ethanoic acid molecule and an ethanol molecule. When these two meet under the right conditions, they can form an ester. There's a diagram that often shows how these three things – the ethanoic acid, the ethanol, and the resulting ester – are related. It helps to see how the atoms rearrange themselves during the process. This kind of visual aid can really make the whole idea click into place, so to speak.
So, the making of an ester involves a specific kind of chemical joining. It’s where an alcohol and an acid come together, and as they do, they shed a water molecule. This is how a new functional group, the ester group, is formed. This group is what gives esters their particular properties and allows them to be used in various ways, which we will get to in a moment. It's actually a pretty common reaction in the lab and in nature.
Where Do We Find Esters in Everyday Life?
You might be wondering where these chemical esters actually show up in your day-to-day existence, right? Well, they are quite prevalent, often in places you might not expect. One of the biggest uses for them is in the industries that deal with how things smell and taste. Think about the pleasant aroma of a ripe fruit or the specific taste of a candy. Chances are, an ester is playing a part in creating that sensation. They are, in a way, nature's own flavor and fragrance creators.
Many of the distinct smells we associate with fruits, like bananas, pineapples, or apples, come from different kinds of esters. These compounds are responsible for those fruity notes that make things so appealing. So, when you enjoy the sweet scent of a strawberry, you are, in fact, experiencing the work of tiny ester molecules doing their job. They are also used in perfumes and colognes to give them their characteristic pleasant odors.
Beyond just smells and tastes, esters also appear in things like fats and oils. These are often complex esters, meaning they are made from larger acid and alcohol components. They are a very important part of how living things store energy and build structures. So, whether you are cooking with oil or just looking at the fat on a piece of meat, you are encountering esters, just in a different form.
They are also found in some plastics and fibers, like polyesters. These materials are made by linking many ester units together in long chains. This gives them strength and durability, making them useful for clothing, bottles, and many other manufactured items. So, from the clothes you wear to the food you eat, esters are, more or less, all around us, playing various roles that make our lives a little more interesting.
The Scent and Flavor of Esters – What About "OnlyFans"?
When people talk about the "onlyfans" of chemistry, they're probably not talking about the chemical compounds, but it’s interesting how a search term can lead us to a completely different kind of "fan" – the fans of a good smell or taste, you know? Esters are very much the stars in the flavor and fragrance business. They are the go-to compounds for creating artificial fruit flavors and pleasant scents. Think about that banana candy or that apple-scented air freshener; an ester is usually the secret ingredient giving it that familiar essence.
These substances are, as a rule, also derived from carboxylic acids, which we touched on earlier. The way their atoms are arranged, especially where the second oxygen atom connects to another carbon atom, gives them their unique properties. This specific connection is what allows them to carry those distinct smells and tastes that we enjoy so much. It's a very particular molecular structure that makes them so useful in these industries.
The names for esters often give us a clue about the lengths of the carbon chains within their molecules. These names include prefixes that tell us how many carbon atoms are in certain parts of the ester. This naming system helps chemists identify and classify these compounds. So, when you see a name like "ethyl acetate," it tells you something about its makeup, which in turn gives hints about its smell or taste. It's a bit like a chemical code, if you will.
So, while a search for "ester ana onlyfans" might lead you to unexpected places, it's worth appreciating the role of chemical esters in making our world smell and taste a little better. They are a pretty big deal in how we experience many of the pleasant sensations around us. It’s actually quite amazing how these tiny molecules have such a large impact on our senses, isn't that so?
Breaking Down Esters - Is "Ester Ana" a Compound?
When we talk about breaking down esters, we are certainly not talking about a person named "Ester Ana," as that's not a chemical compound at all. Instead, we're discussing a process in chemistry where an ester is split apart. This splitting can happen in a couple of ways: either by using water with a base, like a strong soap, or by using water with an acid. This process is called hydrolysis. It's the opposite of how they are formed, in a way.
When an ester undergoes hydrolysis, it yields two original components: a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. It's like taking apart a building block to get back the two pieces it was made from. This reaction is pretty important in chemistry because it allows us to reverse the formation of esters and get back to their starting materials. This can be useful for making other chemicals or for studying the properties of the original acid and alcohol.
One particular kind of ester hydrolysis, the one that happens in a basic solution, has a special name: saponification. This name comes from the Latin word "sapo," which means soap. And there's a good reason for that, you know? This process is actually how traditional soaps are made! Fats and oils, which are a type of ester, are reacted with a strong base, and this breaks them down into soap and glycerol. It's a very old and useful chemical reaction.
So, while the phrase "Ester Ana" might sound like a name, in the context of chemistry, "ester" refers to a specific kind of organic compound that can be broken down. This breaking down, or hydrolysis, is a fundamental chemical reaction with many practical applications, especially in the creation of everyday products like soap. It's a clear example of how chemistry works to transform one substance into others.
Understanding Ester Hydrolysis and Its Uses
Understanding how esters break apart, through hydrolysis, is quite useful. This process, as we mentioned, can happen with either an aqueous base or an aqueous acid. The result is always the same: you get a carboxylic acid and an alcohol back. This ability to reverse the reaction is pretty handy for chemists. It allows them to control the creation and destruction of these compounds for various purposes.
For example, in the production of biofuels, esters are sometimes created from vegetable oils. Then, through hydrolysis, they can be processed further. This control over their breakdown is also important in the food industry, for example, in how some food products are processed or preserved. It's all about managing those chemical changes to get the desired outcome.
The saponification process, where esters break down in a basic solution to make soap, is a very old and still relevant example of hydrolysis in action. It shows how a seemingly complex chemical reaction can lead to a very common and essential product. It's a testament to how chemical knowledge can be applied to practical problems, making our lives a little easier, basically.
So, when we talk about understanding ester breakdown, we are really talking about a key chemical tool. It allows for the recycling of components, the creation of new substances, and the understanding of how natural processes work. It’s a pretty fundamental concept that has wide-ranging implications in many different fields, from making cleaning products to producing energy.
Why Are Esters Important?
Why should we even care about esters, you might wonder? Well, they are rather important for a number of reasons, some of which we've already touched upon. Their role in giving things pleasant smells and tastes is a big one. Without them, many of our favorite foods and perfumes would lack their characteristic appeal. They are, in a way, the flavor and fragrance architects of the chemical world.
Beyond their sensory contributions, esters are also vital in biological systems. Fats and oils, which are essential for life, are types of esters. They serve as energy storage and structural components in living organisms. So, from the smallest cells to the largest animals, esters play a fundamental role in how living things function and survive.
They are also building blocks for many other chemicals and materials. The ability to form and break down esters allows chemists to create a wide array of products, from pharmaceuticals to plastics. This flexibility makes them incredibly valuable in the chemical industry. They are a kind of versatile chemical intermediate, useful for making all sorts of different things.
So, whether it's the aroma of your morning coffee, the texture of your food, or the materials that make up your everyday items, chances are an ester is involved somewhere along the line. They are truly versatile compounds that contribute to many aspects of our lives, often in ways we don't even notice. That, in itself, is a pretty good reason to understand them, isn't it?
Naming Esters and What That Means for You
Learning how to name esters might seem a bit technical, but it’s actually a way to understand their makeup. There are common names for esters, which are often what you hear in everyday talk, and then there's the more formal system called IUPAC. This system helps scientists all over the world understand exactly which ester they are talking about. It’s like having a universal language for these chemicals.
The names for esters include specific parts that tell you about the lengths of the carbon chains in their molecules. These prefixes act like little labels, describing the structure of the compound. So, when you see a name like "methyl acetate," the "methyl" part tells you about one carbon chain, and the "acetate" part tells you about another. This helps you picture the molecule in your mind, so to speak.
Understanding these naming conventions means you can identify the general arrangement for an ester. It helps you figure out which acid and alcohol likely came together to form it. This knowledge is pretty fundamental for anyone working with these compounds, or even just trying to make sense of a chemical label. It’s a bit like learning the alphabet before you can read a book.
So, while you might have come here looking for something about "ester ana onlyfans," the actual chemical "ester" has a rather interesting story of its own, including how we name and identify it. This naming system is a key part of how chemists communicate about these important compounds, ensuring everyone is on the same page when discussing their properties and uses.
This article has explored the chemical compound known as an ester, a substance derived from acids where a hydrogen atom is replaced by another group. We discussed how these organic compounds react with water to produce alcohols and acids, with carboxylic acid derivatives being the most common. The formation process, involving alcohol condensation and acid with water loss, was explained, along with their primary use in the flavor and fragrance industries. We also covered the structure of esters, including the bonding of the second oxygen atom to another carbon, and how their names reflect the lengths of their carbon chains. Finally, the article touched upon ester hydrolysis, including saponification, which yields carboxylic acid and alcohol.
Related Resources:
Detail Author:
- Name : Alyce Treutel IV
- Username : leanne.sipes
- Email : luettgen.malvina@gaylord.com
- Birthdate : 1971-02-13
- Address : 7103 Larkin Tunnel Suite 764 Port Cletamouth, AK 61059
- Phone : 301-297-6965
- Company : Doyle-Fritsch
- Job : Music Director
- Bio : Ipsa molestiae voluptatum autem ut omnis fugit. Id explicabo qui voluptas nostrum aut. Unde est voluptates earum. Veritatis qui ad explicabo autem nulla et voluptates.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/zackary_mertz
- username : zackary_mertz
- bio : Placeat et officia et reiciendis. Consequatur velit aut amet quisquam aliquid qui. Et sunt consectetur mollitia nisi sapiente sunt ut.
- followers : 6996
- following : 1422
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/zackarymertz
- username : zackarymertz
- bio : Soluta exercitationem laudantium ratione nulla laborum omnis.
- followers : 4726
- following : 1019